With the rapid developments and technological advancements that have become much faster, addiction is turning into a persistent problem affecting millions and millions of people across the world. The increasing pressure in modern lifestyles to live under statistically impossible demands of work and constant action makes addiction a rising condition among individuals.
Addiction is a condition that is very multi-dimensional, extending beyond mere substance abuse, and has had alarming effects on families, communities, and society as a whole.
Addiction has emerged over the years as a mental health challenge and continues to contribute to the rapidly alarming speed with which it affects an individual and those around them. The aspects of addiction are so complicated that corrective approaches are very challenging.
The whole blog aims to float a deeper focus on this pressing crisis while laying bare the scientific underpinnings behind it. This blog will discuss everything about craving and addiction types and practical strategies for effective craving management.
Understanding Addiction
In simple terms, addiction is a chronic condition that involves a desire to use a substance or engage in an activity despite its harmful effects. This condition alters one’s brain chemistry and may develop among individuals due to various reasons. Addiction is a pervasive crisis that affects one’s physical, mental, social, and financial well-being.
Types
Did you know that addiction is not only pertain to drug or alcohol addiction?
Addiction is a condition that goes beyond dependence on physical objects only and includes various new-age addictions like gambling or phone addiction. The two major types of addiction are:
Substance-use disorder
Substance-use disorder, which was formerly known as drug addiction , is a type of addiction where persistent use of a substance negatively impacts your health as well as the quality of life. The problematic pattern of substance use can change one’s brain functions over time and, in many cases, is life-threatening.
Substance-use disorder usually involves abusive use of substances like drugs, alcohol, or chemicals that result in addictive behavior for individuals. This type of addiction can affect a person in a mild, moderate, or even severe manner. A few commonly used substances that lead to addictive behavior include drugs, alcohol, nicotine, and other stimulants such as cocaine, etc.
Behavioral addiction or New-age addiction
Another major type of addiction is called behavioral addiction. Also known by the name non-substance addition or new-age addiction, behavioral addiction is a type of addiction that can develop among individuals due to an activity that has the power to stimulate the brain’s reward system. This type of addiction involves engaging in an activity persistently despite its negative consequences on one’s quality of life. A few common activities that can stimulate the brain’s reward system to develop as addiction include gambling, social media use, pornography, gaming, etc.
The science of addiction
Brain Chemistry
One of the major changes addiction causes is in the chemistry of the brain. The use of substances like alcohol, drugs, etc, leads to the release of the neurotransmitters in the brain, mostly dopamine and serotonin. Dopamine, commonly known as a ‘feel-good’ neurotransmitter, plays a major role in the brain’s reward pathway. It creates feelings of pleasure, motivating individuals to reinforce a behavior that often results in substance abuse.
Reward Pathway
The reward system in the brain is one that aims at encouraging behaviors that promote the well-being of an individual. However, this system gets disrupted due to addictive behaviors that overwhelm the brain with dopamine release. This results in a heightened level of cravings as the individual tries to look for the same pleasurable feeling. This finally leads to tolerance, meaning that a larger amount of substance is required to produce a similar reaction.
Genetic and Environmental Factors
Both genetic predisposition and environmental factors play a significant role in making people vulnerable to addiction. Research shows that genetic factors contribute 40-60% to making people susceptible to addiction. Other factors that can further contribute to the development of addiction among individuals include environmental factors ranging from bad childhood experiences or traumatic events in a person’s life.
The cycle of addiction
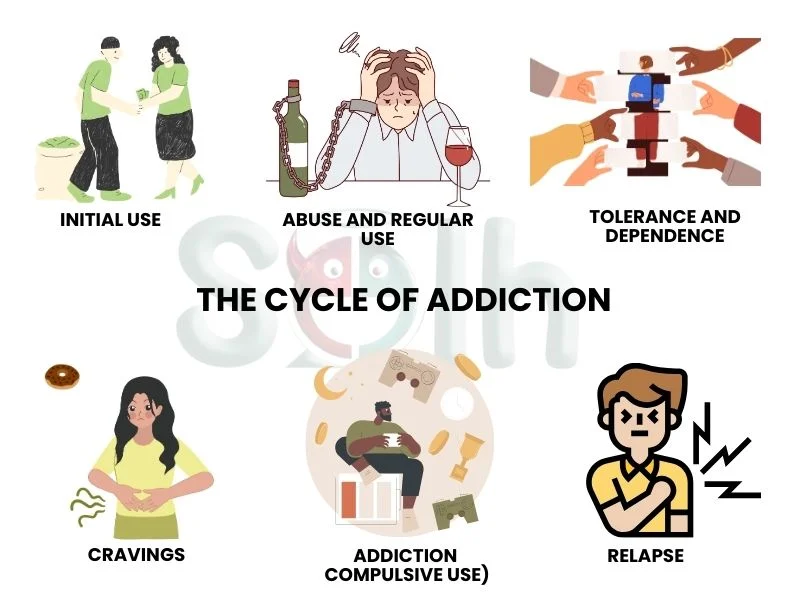
There are many stages at which addiction develops among individuals. Where things start from the initial use, they develop into dependence, which finally results in addiction. The cycle of addiction comprises many stages, including Initial use, Abuse, Tolerance, Dependence, Addiction, and Relapse. Understanding these stages is important to learn and engage in effective strategies to embark on a healing journey.
Initial Use
The cycle begins with the primary use of a substance or participation in a behavior. In some cases, this primary use is a voluntary and experiential choice by the user that is motivated by curiosity, peer pressure, or the backdrop of escape from stress. In other cases, it may be a prescription that eventually involves misuse. At this stage, the person may not be considered as an addict but will enjoy positive reinforcements such as pleasure or a sense of relief from the said stress, thus laying a platform for continued use.
Abuse and Regular Use
At the moment when individual begins regular use of the substances or behaviors, he/she will actually enter the stage of abuse. Regular use is characterized by increased mental and behavioral reliance on substances or activities to cope with life's challenges.
Tolerance and Dependence
As the individual continues to use the substance or engage in the behavior, they develop tolerance. In other words, the brain adapts to the presence of the addictive stimulus, and larger doses or more frequent engagement are required to achieve the desired effects. Eventually, the person may become dependent—both physically and psychologically. Physical dependence is a situation in which the body has become so accustomed to the drug that to suddenly withdraw it will result in unpleasant and sometimes very dangerous withdrawal symptoms.
Cravings
Perhaps the most challenging aspect of addiction is cravings. These uncontrollable urges to use the substance or engage in the addicting behavior are driven by changes in the brain chemistry, particularly in the reward and stress systems. Sometimes, cravings are triggered by external cues.
Addiction (Compulsive Use)
At the summit of the extinguished cycle stands addiction, by which compulsive use takes ownership. By this point, their behavior is, from that point onward, primarily founded upon the need to satisfy cravings and awful withdrawal symptoms. The addictive substance or behavior ultimately takes center stage, overshadowing other responsibilities and relationships.
Relapse
Relapse is a common part of the cycle of addiction and is not a sign of failure. Most people will experience multiple periods of engaging in addictive behavour once more during their recovery process. Relapse happens when the individual is away from substance abuse for a while and gets back to the use after encountering some stimulus or urge power that they cannot or did not handle.
Regression triggers a cycle of guilt and shame and despair and the cycle could continue if not handled appropriately. Key lessons from this discussion include the fact that relapse is a common outcome in recovery and serves as a learning ground on how to handle the problem.
Coping Strategies
While understanding the scientific side of addiction is crucial, one needs to focus on successful coping strategies to deal with cravings. Since both approaches have their benefits, it is essential to develop a combination of a few that might allow an individual to deal with a multitude of problems in the path of recovery .
Mindfulness and Meditation
Mindfulness and meditation lessons can be immensely useful in regulating cravings. Mindfulness practice increases reaction-awareness and enhances emotional regulation that allows individuals to observe the cravings in a pragmatic manner, where cravings are merely temporary feelings that do not require a response. Mindfulness lowers impulsivity and enables individuals to reprieve themselves from taking on an addictive behavior.
Healthy Distractions
Distraction is an effective way to navigate cravings- the more engaging the distraction, the better the strategy. Very productive activities such as painting, gardening, reading, and playing instruments can bring fulfillment in our lives and a void for addictive behaviors to fill.
Social Support
Lean on support from family and friends, or join support groups. Sharing with friends and family provides the trauma during recovery. Certainly, this is the most supportive remedy to fight cravings- a sense of acceptance and belongingness mitigates the feeling of loneliness and fuses fellow-feeling.
Exercise
Exercise is the most effective way to banish cravings. Physical activity releases endorphins that regulate feelings and initiate wellness. Exercise-induced endorphins/ mood boosters can support an overall attitude and diminish the odds of relapse.
Wellness
Making healthy food choices is important for maintaining mood levels and reducing cravings. Selenium and tryptophan-rich foods may work with the body's chemistry to keep all functions running smoothly. Added guidance includes drinking plenty of water instead of caffeine or sugar-laden beverages to supplement or offset strong urges induced by addiction.
Journaling
A journal entry about cravings and emotional triggers can be a useful way to track their development. Write your thoughts and feelings down to help you reflect. That should help you recognize patterns that might lead to temptation and develop strategies to nip them in the bud. Journaling is also an ideal therapeutic outlet for releasing pent-up emotions.
A Professional Approach
The last remaining act to leave in a workbook is counseling or therapy . There exist endless options in this direction, such as cognitive behavioral therapy, which can help one manage cravings and navigate the complexities of addiction.
Conclusion
It is of paramount importance that to understand the diverse aspects of this condition, one has to comprehend the scientific behind it. The study of the addictive process is complex, extending from brain chemistry and the process of craving to strategies for overcoming addiction. Addiction is more than just a question of being strong-minded. It involves significant biological and psychological factors.
Managing Craving requires time, efforts, and effective strategies to overcome. Individuals can go through the recovery process with the help of mindfulness, support networks, or looking for professional help to navigate their journey well.
It is important to remind that anyone who feels they or a loved one is struggling with addiction it is okay to seek help. One should not hesitate to share their experience and reach out to ask for help whenever they feel.
Solh understands. We offer a variety of features to help you invest in self-care and stress management.
Journaling for Self-Reflection: Sometimes, not being able to care for yourself can come from a lack of self-understanding. Solh's journaling feature allows you to explore your thoughts and feelings in a safe space. By reflecting on your experiences and desires, you can gain clarity on what is stopping you from self-care.
Anonymous Support Groups: You are not alone. Solh's anonymous support groups connect you with others who understand the struggle. Share your experiences, find comfort in solidarity, and iscover new perspectives on overcoming the hurdle to indulge in self-care.
Solh Buddy: Feeling lost or disconnected? Your Solh Buddy, a personalized virtual companion, is here to provide encouragement and support. It can offer prompts, celebrate your victories, and remind you of your strengths as you navigate the journey towards self-care.
Talk now: Sometimes, self-care can overwhelm you. Solh's talk now feature gives you access to dedicated counsellors who can help you navigate such situations.
Solh believes in a unique approach to introducing self-care. We empower you to take charge of your well-being by offering a variety of tools. Explore Solh today and discover the power of self-reflection, connection, and support in overcoming any problem of the mind. You are not alone on this path.








